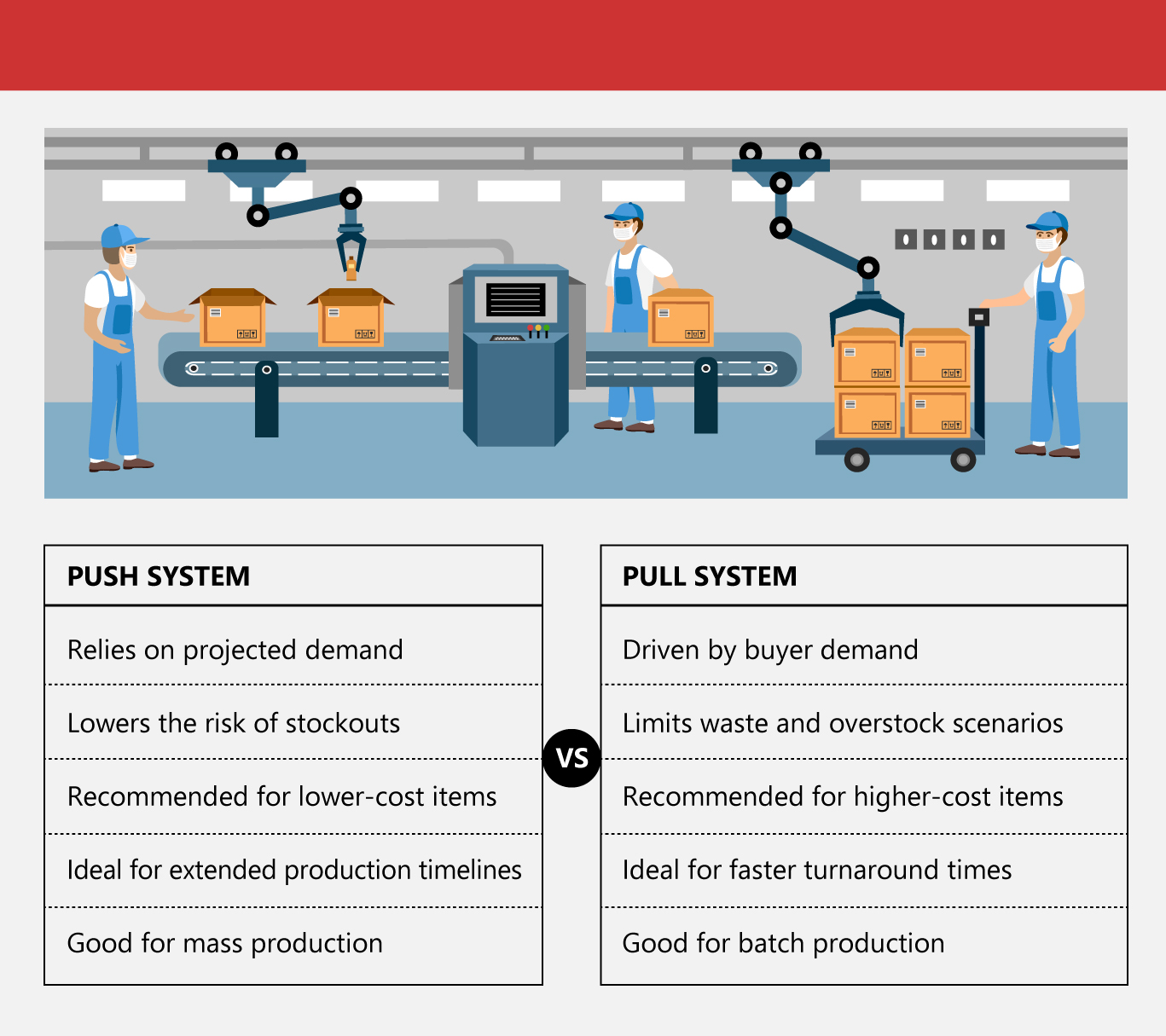
Push or Pull: Which Is the Best Production Strategy

Global manufacturing demands a delicate balance between costs and revenue to maintain financial stability. While this may seem straightforward, manufacturers understand the complexity of this task. Pursuing lean manufacturing further heightens the challenge, requiring precision and efficiency to optimize resources.
Should you push or pull?
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted industrial manufacturing, exposing weaknesses in supply chains and production systems. Material shortages, shutdowns, and transportation delays left customers unable to access desired products. In response, many manufacturers overproduced and stockpiled inventory.
As the industry stabilizes, manufacturers are rethinking production models. Push systems produce goods in anticipation of demand, risking overstock, while pull systems focus on actual customer needs, reducing waste but requiring agility. Choosing the right approach is now key to streamlined product design and development.
What is a push system?
Push systems in manufacturing rely on forecasts and market predictions to guide production, making them ideal for industries with longer lead times and complex, high-variety products. They enhance operational efficiency by producing large batches at maximum capacity, often for make-to-stock (MTS) scenarios, ensuring readiness for anticipated demand.
Advantages of push manufacturing
-
Greater agility
A push system relies on demand forecasts to plan production schedules, ramping up output when an increase in market demand is anticipated. This approach supports design for manufacturing by refining processes and ensuring supply chain members and production teams can meet projected needs.
-
Additional time for strategy and troubleshooting
This system provides ample time for purchasing and replenishing raw materials, as well as for planning and organizing shipping and storage solutions. This proactive technique helps mitigate supplier delays, ensuring smooth operations and manufacturing excellence.
-
Quicker order processing
By quickly delivering products to customers, manufacturers maintain a steady inventory. This strategy improves economic value and eliminates delays caused by fluctuating market demand, ensuring that products are readily available and can be shipped immediately upon order.
Disadvantages of push manufacturing
-
Risk of excess inventory
After the pandemic, many manufacturers experience the drawbacks of a push system, particularly excess inventory that no longer meets market demand. This issue is especially challenging for businesses dealing with perishable goods or items that quickly lose relevance.
-
Challenges in forecasting demand
Predicting market demand can be challenging in manufacturing markets and industries, with no guarantee of accuracy. Economic changes can transform anticipated demand into costly overstock scenarios, making it difficult for manufacturers to align production with actual market needs.
-
Greater financial inlay
Manufacturing industries don’t want to incur storage costs for unsold inventory, especially when predicting market demand requires significant upfront investment. For companies with limited resources, allocating funds to manage overstock and inventory storage can be financially challenging, as it diverts operational funds away from other essential activities.
What is a pull system?
A pull system, based on just-in-time manufacturing, produces goods only when there is actual customer demand, minimizing waste and excess inventory. Unlike the push system, it ensures production aligns with real-time orders, optimizing resources. This approach is ideal for steady demand and limited product variety, offering industrial manufacturing solutions.
Advantages of push manufacturing
-
Boosted efficiency
This production model aims to maximize efficiency by bringing in materials only when necessary and starting production based on actual demand. This approach ensures that resources are used effectively, minimizing waste and focusing efforts on achieving optimal outcomes.
-
Lowered inventory and reduced spending
By eliminating the need for excess inventory, organizations save on storage costs. This reduces waste and boosts productivity, particularly in areas that drive value. This aligns well with the needs of the industrial market, focusing on optimal resource use.
-
Better quality
The pull system is rooted in lean manufacturing, emphasizing producing more with less. By focusing on waste reduction, it enhances the ability to produce defect-free goods. Fewer defects lead to higher-quality products, ensuring better outcomes for manufacturers and customers.
Disadvantages of push manufacturing
-
The threat of inventory shortages
While producing only on demand reduces waste, a sudden spike in orders can lead to stockouts. Without accurate demand forecasting, businesses using a pull system may struggle to meet orders, resulting in lost sales and dissatisfied customers.
-
Additional complications
Producing goods just when needed places manufacturers at risk. Effective communication, accurate demand forecasting, and strong supplier relationships are crucial. Without meticulous planning and organization, a pull system can lead to production delays, leaving manufacturers struggling to meet demand in time.
What is a hybrid push-pull system?
A hybrid push-pull manufacturing system aims to combine the benefits of both models. By maintaining a small inventory for unexpected demand spikes, manufacturers can quickly fulfill orders.
Simultaneously, production can be based on historical data and customer trends, ensuring products are available when needed without overstocking. This balanced approach allows companies to avoid tying up too much capital in unsold inventory while still being prepared for fluctuations in demand.
However, managing this system requires careful planning. Manufacturers must maintain an adequate supply of materials and components to meet production needs, all while addressing the unpredictability of customer demand.
To stay efficient, businesses often rely on inventory management software and well-trained teams, which can be costly. In essence, the hybrid push-pull system enables manufacturers to be more responsive to customer needs while preventing excess inventory, offering a flexible solution in an ever-changing market.
Which strategy is best for you?
Choosing between push, pull, or hybrid manufacturing systems requires careful consideration of several factors. Work-in-progress inventory is more flexible in a push system, while a pull system regulates it by replenishing only when products are sold.
Inventory costs are lower in a pull system since production is based on actual customer orders, reducing the risk of obsolete stock. Meanwhile, product availability is prioritized in a push system, while pull systems ensure timely delivery based on demand.
For businesses offering product customization, a pull system minimizes unnecessary inventory, and a hybrid approach suits mass customization, balancing both flexibility and cost efficiency.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog



