5G Tech Tensions Rise in Germany

For many months, Germany has been under pressure to create stronger restrictions against 5G technology in the country.
In September 2023, German government officials announced to AFP News (Agence France-Presse) that the country will be considering a ban on parts and components from Chinese manufacturers Huawei and ZTE. The target date for the proposal to remove all Chinese parts in the country’s “core network” was set for January 1, 2026.
This development has come from many months of pressure from other EU countries on stricter restrictions for Chinese-made tech and components.
It’s a delicate situation that poses an impact and implications both political and economic. For those pressed for developments in tech, manufacturing, and EMS news around the world, this announcement should prove interesting because of the tensions that have come up on the heels of Germany’s announcement.
(Also read: Better Together? The Chip 4 Alliance)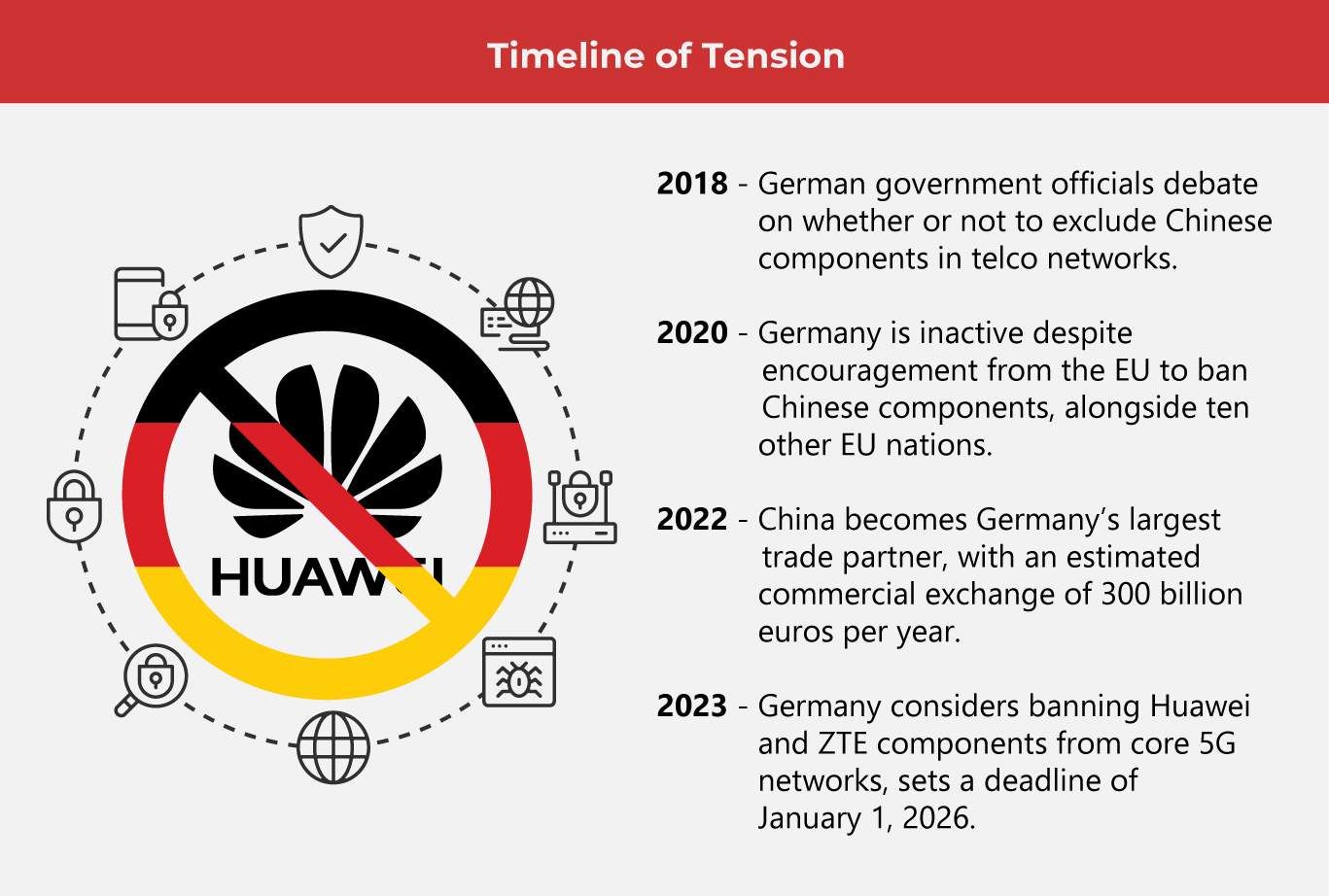
Under Pressure
Reuters reported in June 2023, EU industry chief Thierry Breton urged other EU nations to join the other ten EU countries that have banned Chinese manufacturers Huawei and ZTE from their 5G telecoms networks.
Citing national security concerns and perceived high-risk components in the 5G core network as the reason for the ban, the pressure on Germany to make its stand about its relationship with these manufacturers tightened.
Conflict among government leaders in the country made it more complex. According to an article from CEPA.org, Germany is reviewing its strategies to reduce its reliance on China for raw materials, parts, components, and critical technologies.
Germany’s foreign minister Annalena Baerbock said that the country needs to reduce its reliance on China for “key technologies such as semiconductors, artificial intelligence, and green technologies.” Her statement comes as a more decisive call when compared to the statement made on Twitter by German Chancellor Olaf Sholz that the German government does not want to “disconnect” from China, but to “avoid critical dependencies.”
For Germany, the question of whether Chinese-produced components should be restricted in the country is not new. There have already been discussions regarding this same issue back in 2020 when the EU first brought up excluding Huawei and ZTE from the construction of telecommunications network systems. Back then, Germany did not take any action.
Why did Germany hesitate? There are economic reasons. CEPA.org says that Germany has the strongest economic ties to China among the EU nations. China is Germany’s biggest trading partner, with 228 billion euros in goods exchanged in 2022. The commercial exchange between these two countries per year is 300 billion euros.
Another factor that played a hand here is cost. Huawei and ZTE components and services are cheaper than their European counterparts such as Nokia and Ericsson.
However, the economic and political climate shifted after former U.S. president Donald Trump’s term in the White House. Issues surrounding national security came up as the U.S. government made efforts to soften China’s growing technological influence.
What will happen now?
The decision to restrict 5G technology from Huawei and ZTE was a tough call on Germany’s part. Especially when one takes into account that according to Evertiq, Huawei is responsible for more than half (over 60%) of Germany’s 5G hardware.
This means that more than half of the country’s 5G hardware will need to be replaced, a massive and costly endeavor. The operation to remove all the hardware is estimated at 400 million euros.
However, the country is determined to stick to their guns “at whatever cost.” Several German leaders such as Germany’s Federal Minister of the Interior, Nancy Faeser think that the ban has taken too long and that telco providers “had enough time to adapt to this”.
China, of course, was not happy about this at all. A day after Germany announced considering the restrictions, Beijing said that it “would not sit idly if the German government goes ahead with its proposal.”
The European Commission called Huawei and ZTE “risks” and called on other EU nations to exclude these companies’ components and equipment from their telco services, comments that Huawei strongly opposed and disagreed with. The company criticized the move to restrict their components from being used.
With Germany on board, will more EU nations follow suit and ban Chinese components and equipment? How will this impact their trade relationship going forward? Some experts from the Atlantic Council weighed in on this.
Pundits are noting Germany’s strategy of dealing with China as a “partner, competitor, and systemic rival” echo recommendations for “enhancing domestic economic competitiveness” and “strengthening coordination with like-minded partners.”
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog




