Are Bioplastics Better for the Earth?

Plastic is rapidly poisoning our environment (and even our bodies). One solution that scientists are looking into is bioplastics. How much better will these be versus conventional plastics?
The Problem with Plastic
Plastic is ubiquitous. From packaging to furniture, to fashion accessories, and even the small pieces that complete the average electronic device, plastic is simply everywhere. It’s a plastic world we live in, and though its benefits as raw material are many—versatile, durable, sturdy, and cheap, plastic has become a problem.
Plastic poses problems for our environment in two definitive ways: its disposal and its production. Because plastic takes years to break down and decompose naturally, waste plastic that has not been properly disposed of has accumulated in landfills and oceans. This has disturbed many ecosystems and has harmed plant and animal life.
Human life is not exempt from being harmed by plastic waste. When plastics break down, microscopic microplastic fragments could accumulate and enter our lungs.
Perhaps the biggest problem brought on by plastic waste? It has contributed to climate change.
On the other hand, the production of plastic is the fastest-growing contributor to greenhouse gasses. The Center for International Environmental Law (CIEF) says that “plastic refining is among the most greenhouse-gas intensive industries in the manufacturing sector”. World Wildlife Foundation (WWF) Australia summed it up best: “the more plastic we make, the more fossil fuels we need, the more we exacerbate climate change.”
Science is on a quest to seek new ways to make plastic biodegradable, and perhaps Mother Nature holds some vital keys.
(Also read: Recycling Stories from around the World)
What are Bioplastics?
Environmental scientists are looking into greener alternatives for conventional, commercial, and industrial use.
Conventional plastics are made from petroleum and natural gas sources which are non-renewable. This is why production is greenhouse-gas intensive and is getting increasingly more expensive.
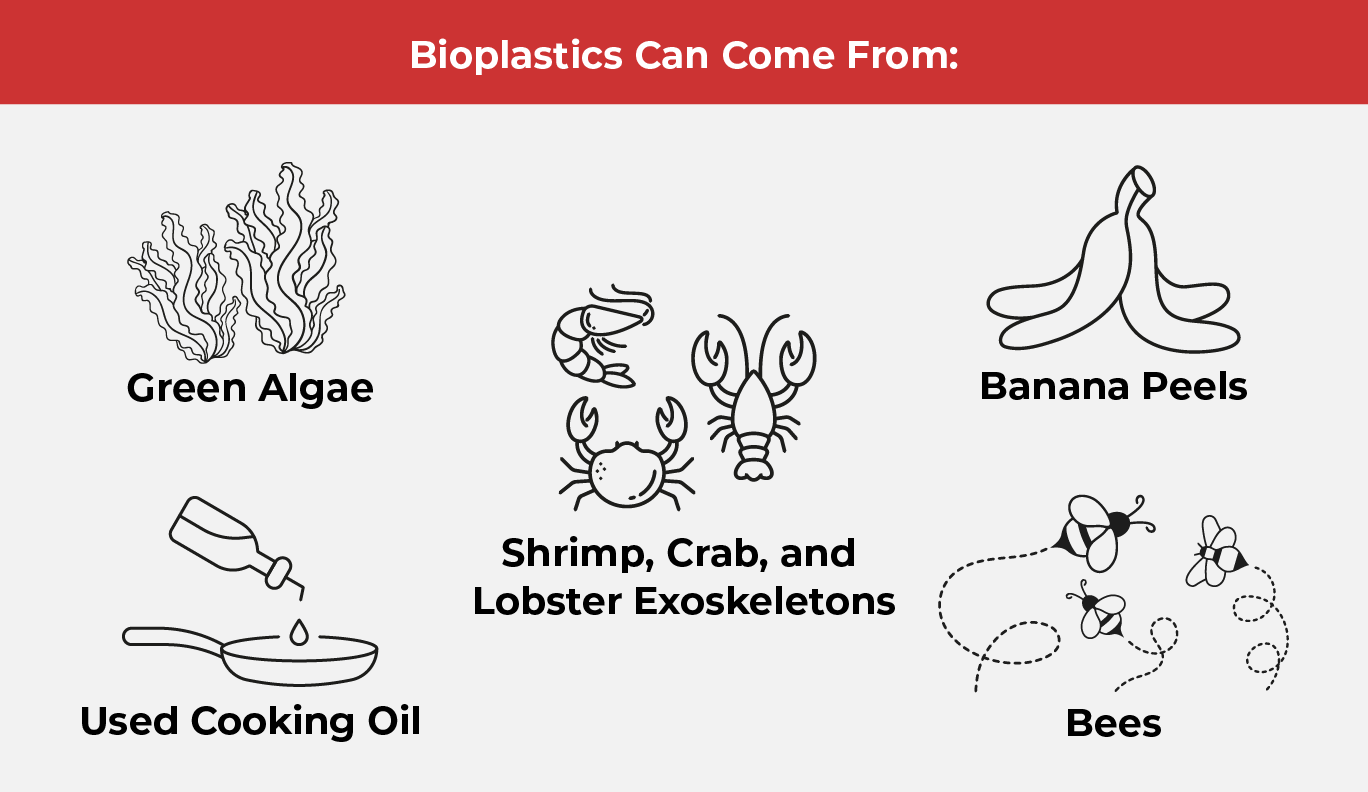
Enter bioplastics. These plastics are derived from plants, animals, and other renewable sources. Cellulose, lactic acid, and even recyclable food waste (i.e., used cooking oil, banana peels) can be sources of bioplastics. Bioplastics can also be made from microorganisms and molecules present in blue-green algae.
Starch and chitosan are also two other sources from which bioplastics may be made. Chitosan is a type of sugar that comes from the exoskeletons of shellfish such as shrimps, crabs, and lobsters. Chitosan is more commonly used in the manufacture of drugs and medicines, but it has gotten the attention of environmental scientists developing bioplastics.
Various studies have found that bioplastics have similar useful properties as conventional plastic, and then some. Scientists like Dr. Mehran Ghasemlou from RMIT University cite “compostability” as one of these properties. Unlike their conventional counterpart, bioplastics easily decompose and blend with natural soil.
In Dr. Ghasemlou’s study, the humble lotus leaf was what inspired the development of bioplastics. Lotus leaves are known to be water-repellant—water slides off easily from the leaf’s surface, cleaning the leaf as the water goes. Dr. Ghasemlou synthetically created a bioplastic that mimics this surface structure to keep itself clean.
Meanwhile, The Los Alaminos National Laboratory has been busy furthering its studies into which algae can produce polymers needed to make plastic. The scientific team has been working with AI to screen polymer chemistries and is using software tools to develop new biodegradable plastic materials.
Fantastic Bioplastic
There is incredible potential for the application of bioplastics in various industrial and commercial fields, such as automotive, building and construction, agriculture, and electronics. However, the largest potential for the application of bioplastics is in packaging; food packaging, to be more specific.
The polysaccharides present in starch and chitosan can be used to create bioplastics for commercial use. Starch has thermoplastic properties that can handle and withstand processing methods. It can also be heat-sealed, which means bags and pouches can be made.
A design company called Morrama has conceptualized a fully biodegradable and recyclable COVID-19 testing kit. Called Eco-Flo, it is made from molded paper pulp and a special bioplastic called NatureFlex film, which can break down more easily than conventional plastic. Apart from the testing kit being made from 100% sustainable materials, it aims to be easier and more comfortable to use than a regular RCT test kit.
Even the toy industry pillar Lego is doing right by the environment by developing toys made out of bioplastics and other sustainable materials.
With all this research surrounding bioplastics currently ongoing, and more fields of other industries opening themselves up to using this over conventional plastic, we can only hope that this can positively impact our environment. Bioplastics are currently being used and mixed in with conventional plastics, but we hope that big industries take advantage of the research and studies made supporting bioplastics over conventional plastics.
According to MarketWatch, the shift towards environmentally friendly products is what’s driving the bioplastics market, and it’s a market that’s continually expanding. The challenge? The recycling process for bioplastics is complex and difficult to maintain. A robust infrastructure to support the production, as well as disposal of bioplastics must be established. Otherwise, we may just end up with the same problem we started with: a lot of plastic waste.
As one of the Top 19 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.




