Can Carbon Capture Help Solve Climate Change?

Despite their environmental impact, fossil fuels aren’t going away anytime soon. In the coming decades, the global manufacturing industry will still use this carbon-emitting energy source to meet their demands. A way to mitigate their harmful effects is carbon capture, which some experts see as a significant strategy to address global warming.
It has become a global mission to resolve the climate crisis—an initiative backed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, which calls on nations to develop technologies to eliminate carbon from the atmosphere. This is in conjunction with the Paris Agreement’s goal to keep future temperature rises to a maximum of 1.5°C.
Enter carbon capture, a promising technology that can potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 14%. This is a target that needs to be achieved by 2050 to significantly reduce carbon pollution in the commercial sector.
Carbon capture and storage explained
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) works by catching greenhouse gas emissions from industrial practices such as manufacturing goods, which uses much fossil fuel-burning energy. The captured energy is then transported and stored deep into the ground so as not to harm the atmosphere. Here is the three-step process in detail:
Step 1: Capturing carbon dioxide
This step separates over 90% of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the other gasses generated in commercial facilities and power plants. Before, CCS was only used in specific industrial procedures to extract CO2 as part of their regular operations. So that more manufacturers can employ this process, previous carbon capture procedures were modified into these popular methods:
- Pre-combustion
Instead of combusting fuel, this process converts it to gas, yielding a synthesis gas composed mainly of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. A further reaction turns the carbon monoxide into CO2. Then, a physical solvent is used to detach the CO2 from the hydrogen. This process is implemented in power-generating settings with an integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) power station that combusts hydrogen in a turbine. Meanwhile, the heat from the exhaust is used to fire up a steam turbine.
- Post-combustion
This method utilizes chemical solvents to detach CO2 from the flue gas produced during the combustion of fossil fuels. This approach is ideal when redesigning operational power plants for CCS purposes.
- Oxyfuel
This process combusts fossil fuel in pure oxygen instead of air to ensure a highly concentrated carbon dioxide capture.
Other ways to capture CO2 include applying ground silicate minerals and rocks on the soil. This speeds up the weathering progress, raising the quantity of CO2 the soil absorbs. Another is membrane gas separation, wherein porous materials are used to segregate CO2 from other gasses. This process is still experimental but shows excellent potential in the CCS technology.
Step 2: Transport
Captured CO2 is typically conveyed through a pipeline or ship to a storage facility. According to the US Congressional Budget Office, the country has around 5,200 miles (8,368 kilometers) of pipelines transporting CO2.
Step 3: Storage
The last step is permanently storing CO2 deep into the ground in geological structures. Other potential locations for storage include:
- Oil and gas reservoirs have been around for millions of years. This means exhaustive research on their safety and efficiency has been done, making them ideal for long-term CO2 storage.
- Deep saline formations are permeable and porous, which allows for the easier injection and detainment of CO2. Because of these formations’ high salinity, injected CO2 becomes more buoyant and effectively contained, minimizing the possibility of leakage.
- Coal beds have natural grooves and fractures, giving extra space for captured carbon. Additionally, coal is highly organic, which has boosted adsorptive qualities—a plus in keeping captured carbon.
Why should we explore carbon capture?
CCS capture is primarily geared toward better environmental health. If we can keep CO2 emissions from penetrating the atmosphere, we can decrease global warming and its effects. These include extreme weather events, ocean acidification, rising temperatures and more. But carbon capture also offers these benefits:
- Economic stability
CCS allows the ongoing use of fossil fuels, minimizing their carbon footprint. This is especially beneficial in areas with little or no infrastructure for sustainable energy, allowing them to continue earning while caring for the environment. Moreover, implementing carbon capture can open jobs across industries like manufacturing and engineering.
- Energy resilience
When a nation diversifies its energy portfolio and ensures its local energy supplies, it doesn’t need to rely on imported energy. This reduces vulnerability to global energy market disruptions, geopolitical events, and trade issues while promoting economic growth.
- Long-term benefits
Captured carbon can be used for valuable products, including chemicals, fuels, carbonates, and oil recovery. In agriculture, the recovered carbon can boost plant and soil health. Sequestered carbon can also create construction materials like concrete and carbon fibers.
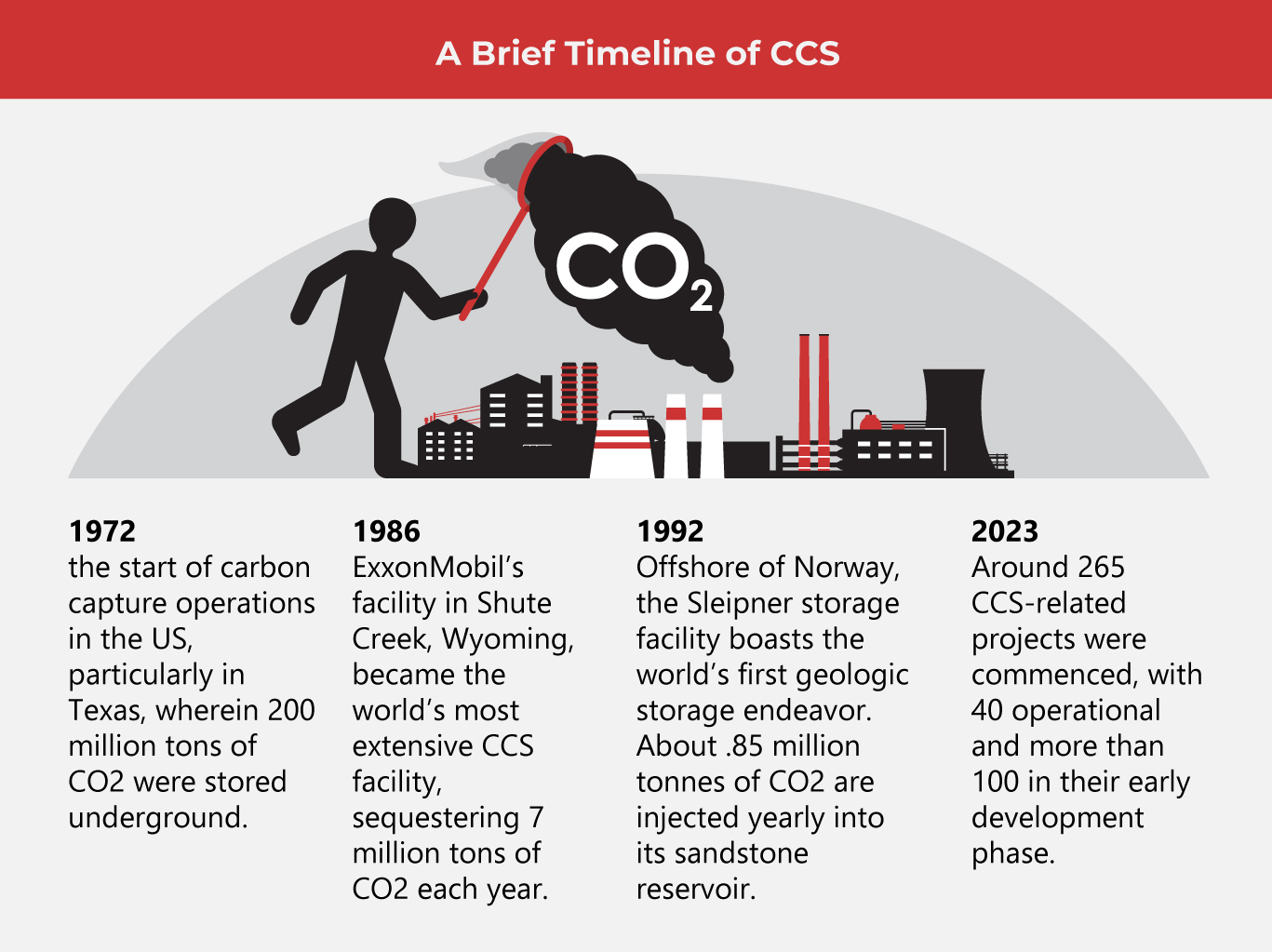 CCS challenges
CCS challenges
Though CCS offers many benefits, especially for the environment, it must overcome multiple challenges. This technology is still emerging, making it costly to set up. Technical difficulties and safety issues may arise, and authorities must ensure storage guidelines and compliance standards. Many are concerned about groundwater contamination, pipeline leaks, and health risks among workers. Also, some may see CCS as detrimental to promoting renewable energy and other energy-efficient methods.
Still, CCS remains a promising way to lower carbon emissions. As technology evolves and collaborative efforts strengthen, its risks and difficulties can be managed. Comprehensive project plans, strict implementation and monitoring can also improve public perception, making its widespread adoption possible.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog




