Factories Made for the Future

While automation, robots, and digitalization have been part of factories for a good while now, what makes a factory a smart one is how interconnected each part of its system is.
A smart factory is comprised of a network of sophisticated machine systems that communicate with each other and are capable of massive computing and learning power as they perform tasks.
(Also Read: Industry 4.0: How to Make Manufacturing Future-Proof)
Today, intelligent automation and digital transformation are touchstones of modern business and industry. Following the sea change brought about by the global pandemic in 2020, businesses have come to value resilience amid uncertainty.
Wanting to ensure business continues smoothly amid turbulent, and oftentimes uncontrollable circumstances, industries look to digital solutions to improve services, address gaps in the supply chain, and add value.
As services improve and become more efficient, end consumers’ habits evolve. Identified as early as 2019 as “the Amazon Effect”, consumers around the world have come to expect expediency when it comes to purchases and deliveries. “Why wait for a week for parcels to be delivered when we can have it the next day” quickly becomes “Why wait the next day when we can have it delivered the same day?” 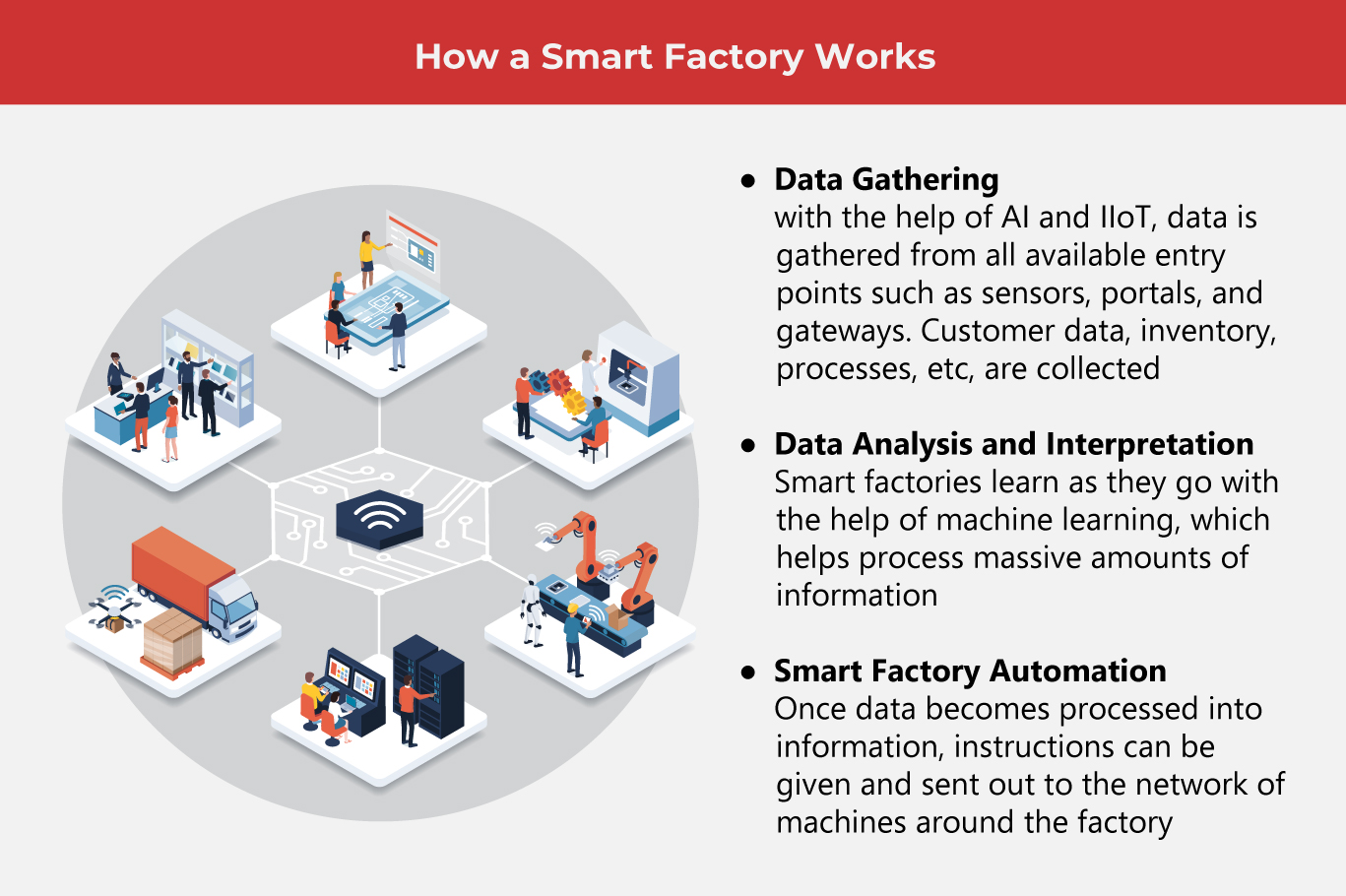 Smart Factory Technologies
Smart Factory Technologies
The smart factory utilizes AI technology, machine learning, Big Data analytics, cloud computing, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Here’s a closer look into the key technologies that run smart factories.
Sensors – Every smart system will involve sensors. Sensors allow data to be collected and are the touchpoints of every smart factory.
IIoT – Industrial Internet of Things refers to how devices and systems communicate with each other, but on a much larger scale than consumer electronics. IIoT is used to run the efficiency of the smart factory.
Cloud computing – This allows large amounts of data to be stored, processed, and shared with the rest of the network in the smart factory.
Big Data Analysis – All sorts of data come in from every touchpoint, portal, and gateway. Smart systems need to be able to crunch the data quickly and make sense of it for actionable steps.
The Smart Factory Four Levels
When it comes to building a smart factory, experts have identified four levels of data structuring to get through.
Level One – Available Data
This level describes the starting point for most factories where data is available but not accessible. Gathering and making sense of all pertinent data manually is time-consuming, and very likely could add to delays and inefficiencies.
Level Two- Accessible Data
A slight improvement from the first level where data is somewhat organized and sorted, though with some limitations.
Level Three: Active Data
On this level, machine learning and AI make data proactive, meaning the data can sort itself out, and generate insights without much human intervention. Here, the system can already make useful predictions (i.e., potential breakdowns) so failures can be avoided.
Level Four: Action-Oriented Data
At this advanced stage, machine learning can provide actionable steps to problems that have been identified at an earlier stage. The system can also act on the solutions generated without much human intervention or interference.
Benefits of a Smart Factory
Smart factories allow businesses to become more resilient, productive, and efficient. According to a study from Deloitte, smart factories help businesses improve their asset efficiency by 20%, product quality by 30%, reduce costs by 30%, and improve sustainability and safety by 10%.
Deloitte says that “a smart factory can optimize performance across a broader network, self-adapt to and learn from new conditions in real- or near-real time, and autonomously run entire production processes.”
Another study says that by 2030, businesses that have smart factories will likely outperform factories with a traditional, less automated system.
When experts talk about sustainability in industrial settings, they are also talking about consumer perception. Today’s consumers are a lot more aware of business practices and we have become more conscious of ethical, as well as green practices. The environment, carbon footprints, and sourcing have become more important to consumers. We want to make sure that businesses are accountable.
Smart factories ensure that checks and balances happen for businesses. Smart factory systems and solutions improve business and manufacturing practices presenting opportunities to shift to better, greener, and more sustainable ones.
When it comes to the safety of human workers, smart factories provide automation for heavy lifting so human workers can focus on other tasks.
Apart from these, business agility, flexibility, faster response time, and customer experience also benefit.  As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog



