How AI Can Fight Fake News

Fake news is our digital world's dirtiest weapon, wreaking havoc online and on the ground. While AI is supercharging its spread and speed, find out how AI can also help stem the tide of disinformation.
The Information Age has ushered in the age of misinformation, disinformation, and malinformation—what we know colloquially as fake news. Powered by the immense speed and reach of the Internet, fake news is today’s dirtiest weapon, used to sow discord and chaos. It undermines trust in government institutions, intensifies social conflict, and incites extremist views.

With rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), it is becoming even harder to identify, investigate, and destroy this web of lies. Deepfake videos with synthetically altered footage can fool you into thinking he really is Tom Cruise or former US president Barack Obama. AI-powered chatbots like ChatGPT, able to produce human-like responses with one click, can mass-produce content for fake news creators. AI bots and social media algorithms spread these false narratives.
In this article, learn how artificial intelligence helps promote the spread of fake news and how, on the other end of this double-edged sword, AI can disarm these campaigns of falsehoods.
AI as a tool for disruption and deception
In this digital era, social media has become the primary source of news online for most people, and it’s where fake news campaigns are deployed to manipulate people’s perceptions and emotions.
The Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), a policy research organization within Georgetown University's Walsh School of Foreign Service, focuses on the effects of AI on national security. In its 2021 policy brief, CSET identifies the key stages of disinformation campaigns. Termed RICHDATA by the authors of the policy brief, it is illustrated as a pyramid to emphasize the importance and value of preparatory stages.
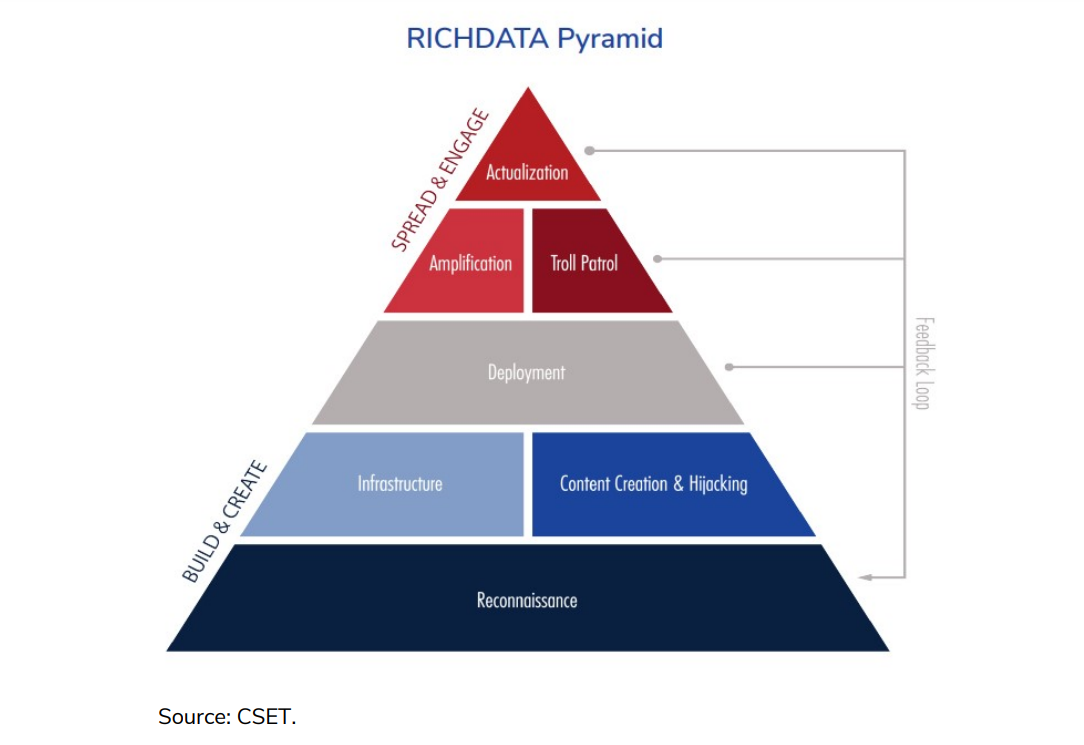
In the “build and create” phase of a disinformation campaign, CSET identifies three stages:
- Reconnaissance: fake news operators monitor the environment to gain a better understanding of their target audience by identifying fissures, mapping audience channels, and mapping and segmenting their target audience
- Infrastructure: operators build the necessary infrastructure for their campaign, such as a digital army of bogus personas, automated accounts, distribution channels (social media pages and groups), and websites to host their false content
- Content: having identified their false narratives and target audiences, fake news operators create 24/7 content that prioritizes visuals and elicits varied emotional responses
With their content and infrastructure in place, it’s time for the deployment of content, whether it be a meme, social media post, blog, or video. These are seeded in specific channels such as a social media page, a conspiracy theory forum, or a fake news website that they manage.
After the deployment of fake news, the campaign enters the “spread and engage” phase:
- Amplification: operators use bots, platform algorithms, and social-engineering techniques to get as many eyes and ears on their message
- Troll patrol: organic and heated debates with authentic users help operators control the narrative and drive up engagement
- Actualization: the disinformation campaign converts and mobilizes unwitting participants
According to CSET, the use of AI and machine learning to increase the speed, scale, and personalization of disinformation campaign techniques is “not only plausible but already underway,” and these technologies, “paired with human operators, may soon enable social bots to mimic human online behavior and to troll humans with precisely tailored messages.”
AI to fight fake news
Researchers, media companies, and non-profit organizations are harnessing the power of AI to prohibit the proliferation of fake news. Here are several ways that they are turning AI from foe to friend.
Text analysis and detection
AI-based tools can do a linguistic analysis of textual content to identify fake news. By searching for cues like word patterns, readability, and syntactic structure, algorithms can distinguish computer-generated from human-produced textual content. AI-based tech can examine a text’s word vectors, word placement, and connotation to identify hate speech. However, with the increased sophistication of generative adversarial networks, it will become more difficult to spot AI-generated content.
Root tracing
Fake news has to start somewhere—a place of origin where it was seeded, took root, and then began sprouting up all over the Internet like weeds. Human editors at fact-checking websites such as Politifact, Snopes, and FactCheck investigate if reports or images are authentic. Once a fake has been identified, AI algorithms search the web for similar information and content.
Spread analysis
According to MIT researchers, fake news travels six times faster on Twitter than real news does. In addition, the chain length—the number of people who shared a social media post—never exceeded 10 for real news but increased to 19 for fake news.
“We found that falsehood diffuses significantly farther, faster, deeper, and more broadly than the truth, in all categories of information, and in many cases by an order of magnitude,” says Sinan Aral, co-author of the study.
While swarms of bots can amplify fake news on social media, humans are also responsible. In this one-click world, it’s incredibly easy to share without pausing for critical thinking, especially when emotions are running high or a person wants to be perceived as being in the know.
GoodNews, a study funded by the European Research Council (ERC), used geometric deep learning to analyze the spreading patterns of fake news on social networks.
“Our experiments indicate that social network structure and propagation are important features allowing highly accurate (92.7% ROC AUC) fake news detection,” the authors of the study share. “Our results point to the promise of propagation-based approaches for fake news detection as an alternative or complementary strategy to content-based approaches.”
Fact-checkers: the heroes of the Web
Newtral, a Madrid-based fact-checking website, developed a multilingual AI language model, ClaimHunter. Using 10,000 statements, ClaimHunter’s developers trained the system to recognize sentences that seemed to include declarations of fact: numbers, data, or comparisons.
“We were teaching the machine to play the role of a fact-checker,” says Rubén Míguez, chief technology officer of Newtral.
ClaimHunter monitors the Twitter accounts of politicians and sends alerts when a factual statement is shared. It also transcribes audio and detects statements for verification.
"We are saving 90% time in political monitoring," shares Míguez, enabling reporters to shift their focus to publishing more fact checks.
But even with technology on their side, fact-checkers are fighting an uphill battle.
“Fact-checkers are often tiny organizations compared to those producing disinformation,” shares Tim Gordon, co-founder of Best Practice AI, an AI management and governance consultancy based in the United Kingdom. “And the scale of what generative AI can produce, and the pace at which it can do so, means that this race is only going to get harder.”
The human factor
“Humans do need to be in the loop. AI is merely a tool for accelerating certain human judgments,” says Daniel Rogers, the executive director and co-founder of the Global Disinformation Index (GDI). It is a non-profit organization that gathers data on how fake news travels and spreads.
“Computers are good at repeating a raw task many times, but anywhere a judgment is involved, you need a human,” says Rogers.
In today’s digital world, we need to nurture a society of critical thinkers: individuals with ingrained fact-checking habits who can detect disinformation and curb its spread. Governments, technology developers, the media, and individuals must present a united front to fight fake news.
As one of the Top 19 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog



