There’s an AI in the O.R.
Robots and AI in medicine are becoming critical in helping surgeons detect diseases earlier, and ultimately make better decisions to save patients’ lives.
The technology behind new soft robots and AI is helping doctors in various specializations improve diagnosis and treatment for their patients. The use of robots and AI is becoming widespread and worthy of further study, specifically in the fields of cardiovascular surgery, endovascular surgery, and orthopedics.
The type of robots being used and developed for the operating room is thinner, softer, and can be guided more easily by the surgeon to reach tight, delicate, hard-to-reach parts in the human body, such as blood vessels, our brains, and inside our lungs.
Some of these robots are high-tech catheters designed for many specific purposes: to help surgeons take a deeper look inside our organs, to administer treatment, or to perform more precise surgery. These robots help surgeons reach what normal instruments can’t.
(Also read: How Robotics is Transforming Healthcare)
Many robots, Many O.R.’s
Robots are instrumental in interventional medicine, allowing doctors to treat patients who would otherwise require surgery to explore other options before resorting to the surgery. Here, robots and AI work hand-in-hand to more efficiently and precisely find out what the patient requires.
Recently, the Korean Institute for Machinery and Materials (KIMM) has developed the country’s first robotic catheter. The guiding catheter can reportedly bend in two directions, whereas it can previously only be bent one way. Its purpose is to lead another catheter to where the surgery needs to be performed without damaging surrounding organ tissue and is intended for deep insertion.
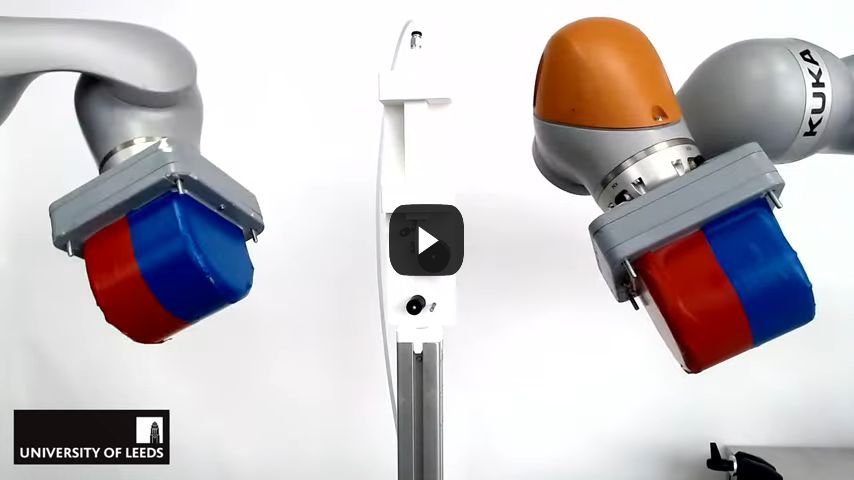
Meanwhile, similar advancements have been made in the United Kingdom, blending soft robot technology with magnetic field technology. This magnetically-guided soft robot resembles tentacles and is designed to direct tumor-killing particles into cancer tissues inside the lungs. It can also be used to guide wires to seek out blood cancers.
Scientists are looking into soft robot technology’s potential for performing wireless surgery. Here, magnets play a big role in steering the robots inside the body toward where they’re supposed to go, improving procedures such as cutting and suturing deep inside the body.
Some robots, such as those used in orthopedics, more closely resemble what we may normally expect robots to look like: big, bulky, sturdy machines. These robots help orthopedic surgeons replace patients’ joints—knee surgery being quite common. Thanks to robots, knee replacements can even be an outpatient procedure today!
Engineers are also looking into the application of rescue and medical robots in large-scale emergencies such as natural disasters and war. Tiny, insect-like robots are being developed for these scenarios. Prototypes with artificial muscle technology are being made to copy bug-like movements so they can get into tighter spaces and survive where larger creatures may not. Remember the movie “Innerspace” from the ‘80s? It’s sort of like that, but with robot bugs instead of a miniaturized person.
Generally, there are three types of robotics systems for surgery: active systems that work autonomously, semi-active (has pre-programmed components but need a surgeon to operate them), and surgeon-driven systems.
Robots and AI in Brain Surgery
Neurosurgery has benefited from the use of robots and AI. In this highly delicate field of surgery, the technology behind their instruments helps improve brain surgeons’ performance., especially in the subspecialty of neurosurgery called endovascular neurosurgery.
Here, catheters and radiology are used to diagnose and treat diseases of the nervous system. A group of endovascular surgeons, led by Dr. Javier Bravo recently published a medical article reviewing related literature about the study of robotics and AI’s applications in endovascular surgery. This article cites many successful cases and examples of how robotics and AI have been applied to help their patients and to further research and study various neurological conditions.
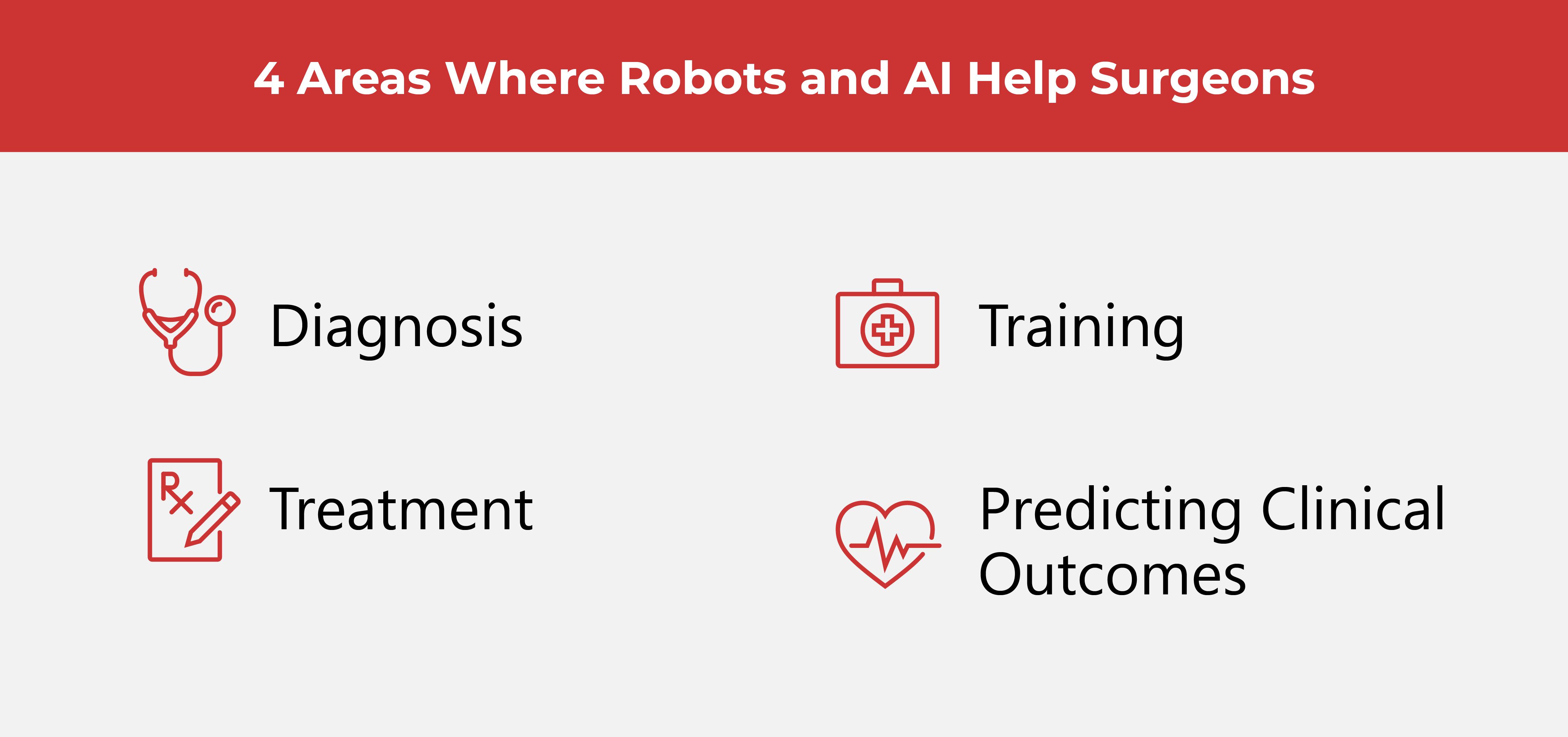
Their review showed four areas where robotics and AI have shown their effectiveness: diagnosis, treatment, training, and predicting clinical outcomes. Stroke patients benefited from earlier diagnoses thanks to AI. The review cites machine learning and deep learning algorithms effectively detecting aneurysms and other life-threatening conditions.
When it comes to treatment, this review builds a strong case for the use of robotics and AI in endovascular surgery. An important advantage mentioned was “improved stability of the catheter tip”, which decreased the number of movements needed, and “enhanced performance” by helping the surgeon make their way through the vascular anatomy. It also decreased radiation exposure for the surgeon.
Meanwhile, robotics systems such as the da Vinci robotics system were mentioned in the review as being “proven to boost surgical precision”.
Training is another important area where robotics becomes a tremendous help. Pre-surgery rehearsal has been observed to improve a surgeon’s performance.
Lastly, AI algorithms help predict clinical outcomes and allow doctors to predict possible complications following procedures and treatments. The review goes on to say that “Artificial Intelligence and robotic systems have transformed the practice of medicine, allowing for time-effective diagnosis, efficient patient categorization and treatment, improved diagnostic accuracy, and precise and safe surgical interventions.”
Next Steps and Challenges for Robotics in Surgery
Some surgeons cite the lack of “sensation” and “haptic feedback” as being one challenge of using robotics in surgery. This is an understandable limitation, as many robots are still surgeon-driven. It becomes challenging when a surgeon can’t “feel” the device as it’s being inserted into the patient. The surgeon must rely on visuals over touch when it comes to guiding the instrument. This is one area that is worthy of further study and improvement.
Another challenge for surgeons and patients is the cost entailed in using this technology in treatments. According to one study, the average cost of a procedure using all this technology is $1866. Surgeons recommend further study be done on the cost-effectiveness of robotics and AI in surgery.
Overall, the outlook is good for robotics and AI in ORs. Doctors found that the results of using robotics and AI in their practice have led to an “increase in overall health and quality of life” for patients, which means not only have robots saved lives, they’ve improved life as well.
As one of the Top 19 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.




