China’s Swap Stations Are Charging Up
China has been testing battery swaps for some time, where drivers replace empty EV batteries with fully charged ones. Now it's rapidly expanding stations, helped by its dominance in EV battery production and the electric automotive market. This simple solution could ease range anxiety and cut down charging time.
As electric vehicles (EVs) go mainstream, faster and easier charging is in high demand. Battery trends like swapping offers a quick fix by letting drivers trade empty batteries for full ones in just minutes. The tech is still new, but China is leading the way, especially with heavy-duty trucks, and is now testing it for everyday cars too — a future-ready move in EV innovation.
Nio has emerged as the frontrunner in China’s battery-swapping scene, building over 3,000 swap stations and powering strong EV sales. In 2023, the company experienced a major milestone in China, delivering over 220,000 EVs—a notable increase of 40% compared to the previous year.
This rapid growth has been fueled by its expanding swap network, which now makes up nearly 70% of all battery swap stations in the country. On top of that, Nio has also boosted its charging infrastructure and test solutions, with more than 25,000 charging points now available across the country.
Meanwhile, CATL, China’s largest EV battery maker, is partnering with oil giant Sinopec on system integration to create a nationwide battery-swapping ecosystem, aiming to advance the market.
(Also read: Can Trump Break the EV Industry?)
Advantages of battery swapping
Battery swapping offers a new approach that changes the way EVs recharge and keep moving.
-
Shorter travel delays
Battery swap stations can replace a depleted battery in three to five minutes, improving operational efficiency. In contrast, EVs often require 10 to 15 minutes of quick charging to reach 80%, with standard charging taking even longer. This fast turnaround makes battery swapping attractive for drivers and passengers who want minimal downtime and quicker trips.
-
Higher rate of EV adoption
This development helps more people switch to electric cars by easing worries about running out of power during long trips. In the early days, EVs were hard to promote because there weren’t enough charging spots, causing long waits and trip delays. Battery swapping quickly became a way to fix this, boosting manufacturing markets.
-
Charging flexibility
Battery swap stations allow drivers to quickly exchange depleted batteries for charged ones without waiting. This reduces the need to plan trips around charging stops and eases access issues in areas with limited charging infrastructure. As the system grows, it also creates new opportunities for automotive parts suppliers to support the development of swappable battery tech and related components.
-
Potential power storage facilities
Another possible benefit of these stations is grid stability. As China’s renewable energy market grows, storing solar and wind power becomes essential. These stations could act like backup batteries, storing energy and releasing it when demand spikes or outages hit. Some companies see profit potential too, by selling power when prices are high.
-
Lowered costs
Sustainability is a key benefit of battery swapping, as it separates battery ownership from the vehicle. This lowers the upfront cost of EVs and promotes shared battery use. With centralized management, batteries can be better maintained, upgraded, and recycled—reducing waste and extending their product life profile while making EVs more accessible and environmentally friendly.
-
Battery standardization and maintenance
One challenge with EV batteries is the lack of common standards—different models use different battery types, making things harder to manage. Battery swapping helps solve this by using shared, well-maintained battery packs. Standardized batteries simplify test and system development, making it easier to monitor performance, charge safely at central hubs, and support recycling or second-life use.
(Also read: Why China is Winning the EV Race)
Barriers to battery swap station growth
Battery swapping stations offer exciting benefits, but they also face several challenges that could slow their growth and wider adoption.
-
Compatibility issues
Not every EV can use battery swapping because the stations need to match the car’s battery system. Right now, this method is mostly used by commercial vehicles like taxis and delivery trucks, not regular cars.
-
Ownership concerns
Battery ownership is a challenge for swapping because drivers must give up their specific battery and might receive an older one. To solve this, some companies let customers buy cars and rent batteries separately.
-
Business risk
This model means automakers must invest heavily in managing many batteries, tying up money and increasing risk. The need to own and maintain large battery stocks adds financial pressure, making it harder for swapping stations to expand.
-
Land scarcity
Swap stations need lots of space and power, which is limited in busy areas, slowing growth. Building them is costly and requires teamwork. But some petrol stations are now converting to support battery swapping, easing expansion challenges.
Why China succeeded
China has quickly become a leader in the battery-swapping market, setting a pace that many other countries are striving to match.
-
Government support
China’s government helped drive the growth of battery swapping and industrial manufacturing solutions. Through subsidies and pilot programs, it has encouraged companies to build stations and produce compatible EVs. Provinces like Hainan offered to cover 15% of equipment costs for new stations. Backed by national goals to lower emissions and boost clean tech, cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou have embraced battery swapping as part of a broader push for sustainable transportation.
-
Key partnerships
NIO has partnered with a state-owned company backed by Beijing’s Changping district to build 100 battery swap stations. The project will expand as part of a wider push to develop a green energy swap system. This move follows NIO’s recent collaboration with battery giant CATL to create the world’s largest battery-swapping network. With strong support from both local government and major industry players, NIO is accelerating its efforts to grow clean energy infrastructure in China.
-
Lithium-ion industry
China’s rapid rollout of battery swap stations is partly due to its strong battery supply chain management. As a global leader in lithium-ion battery production, the country benefits from a steady, affordable battery supply. This efficient control of sourcing and manufacturing lowers costs and makes large-scale battery swap networks easier to build and maintain, giving China a major advantage in expanding its electric vehicle infrastructure quickly and effectively.
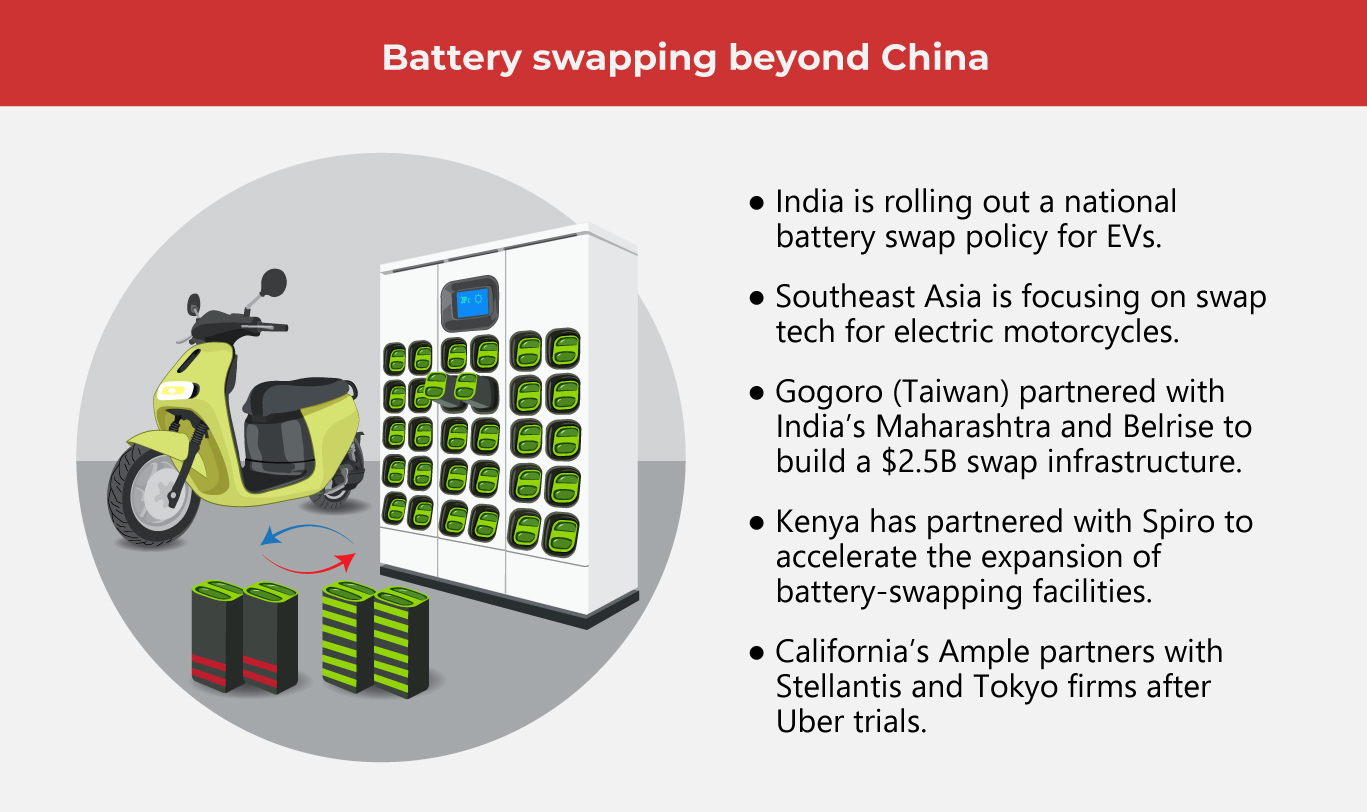 The concept of battery swapping is rapidly becoming more widespread, with its influence extending far beyond China to other global markets. China’s fast rollout has set the pace, showing how this tech can grow with the right support. As more countries explore similar systems, swapping could become a key part of the EV landscape.
The concept of battery swapping is rapidly becoming more widespread, with its influence extending far beyond China to other global markets. China’s fast rollout has set the pace, showing how this tech can grow with the right support. As more countries explore similar systems, swapping could become a key part of the EV landscape.
Some experts believe that by 2030, it could make up 10% of the global EV market, with millions of battery swaps happening every year.

As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog



