EV Charging Stations All over the World
Discover the recent developments in electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure in core areas in the US, EU, Asia and the UK. Learn why there's a need to boost EV charging networks and the challenges this expansion faces.
According to TrendForce, EV charging stations worldwide will triple from 2023 to 2026, reaching a peak of 16 million. The study attributes this rise to more and more people owning neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs), which include plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Additionally, Research Dive predicts that EV charging infrastructure will balloon by a CAGR of almost 35% by 2026 from US$1.7 million to US$18.6 million. The Asia-Pacific market, in particular, reflects a healthy growth of 34.5%, with earnings of over US$5 million during the outlook period.
Climate change mitigation is the main reason countries encourage the use of EVs. However, motorists are also shifting because of the technology's rapid developments, which allow for longer driving ranges on a single charge and more affordable batteries that boost safety.
Countries like Taiwan and China aim to transition away from petrol-powered cars by focusing on green vehicles like EVs to lower global emissions. Car manufacturers also fuel the switch by producing EVs that target users' specific needs and preferences. Research Dive reveals that EV market stakeholders are placing over US$90 million in the industry, which helps drive innovation and the market.
Why is the EV charging station infrastructure expanding?
Charging infrastructure, called charging networks, is a salient part of the EV industry. These stations connect EVs to an electrical source, replenishing the vehicle's power. Some infrastructure provide enhanced functions such as faster charging, mobile connectivity, internet access, and automated metering. EV owners are even exploring setting up charging stations in their garages and parking spaces. This infrastructure is growing because of the following reasons:
- Government incentives
Various governments from different countries have sped up the widespread acceptance of EVs. For instance, the US federal government offers a maximum tax credit of US$7,500 to those who purchase new EVs. Meanwhile, the government of India has shown its support for EV infrastructure by sanctioning the establishment of over 2,600 charging stations in 62 cities. In Tokyo, the government announced its plans to relax its rule on setting up fast-charging stations to enhance the country's charging network.
One effective way to make EVs more affordable is to lower battery costs. Thankfully, manufacturers have addressed this through numerous battery technologies that make EVs safer, more efficient, economical and eco-friendly. One innovation that's making waves is the lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery, which promises increased energy density, a long lifespan, and a cobalt-free composition.
Also read: How EV Batteries Are Tested
- Addressing range concerns
One of the top concerns that keep motorists from switching to EVs is range anxiety, the fear of exhausting the battery before reaching a charging point. The growth of charging stations can assure EV owners that they have plenty of opportunities to recharge their EV batteries, allowing them to reach their destination confidently.
- Green technologies
Both manufacturers and users are looking to reduce their carbon footprint. Clean power equipment includes solar-powered charging stations, which, according to Research Drive, do not require building permits. This means a faster installation of charging infrastructure, coupled with significant R&D investments by top industry players, results in the global market's expansion.
But what can keep this market from flourishing? Rigorous installation requirements and high infrastructure costs remain the biggest challenges of the EV charging infrastructure industry.
How the world gears up for EV charging infrastructure development
If EV charging stations grow three times within three years globally, there will be six vehicles for every charging point in 2026—a substantial decrease from the 10:1 ratio in 2021. Different countries have unveiled their initiatives to intensify this market.
China
China realizes that battery production is crucial in amplifying the public adoption of EVs. Currently, the country houses over 100 gigafactories, which are massive manufacturing facilities that churn out huge quantities of batteries. At the same time, China plans to achieve their vehicle-to-charger ratio target of 2:1 in 2030.
Europe
The EU announced the construction of 50 battery gigafactories. France, in particular, announced its offer of €1.5 billion worth of loans to set up four gigafactories. Regarding charging stations, Europe plans to construct 17 million by 2030. This equates to a vehicle-to-charger ratio of 9:1 at the end of the forecast period.
The EU council has released new mandates to encourage the use of EVs, including installing fast chargers that generate at least 150 kilowatts every 60 kilometers along the Trans-European Transport Network by 2026. Meanwhile, the core road network, which connects major urban centers and hubs, must have a minimum combined output capacity of 400 kilowatts, including a charging station that offers 150 kilowatts.
United Kingdom
EVs have strong sales in the UK, comprising almost 17% of new vehicle registrations in 2022—an increase from just 0.4% six years prior. As of June 2023, over 44,000 charging stations were built in the UK, of which over 8,680 provided fast charging. The government announced its goal of 300,000 charging points of various speeds by 2030 to speed things up. Though the number of charger installations is steadily increasing monthly, annual output should double by 2025 for the government to meet its target. Adding to the pressure is the demand from the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders to build 2.3 million charging points by 2030.
United States
The US has more than 200,000 charging points, which the federal government hopes to more than double in three years. If 500,000 charging stations are built by 2026, with approximately 15 million EV owners, the vehicle-to-charger ratio will be 32:1. A
These developments address range anxiety while allowing for more simplified contactless payments—minus subscriptions and apps— at stations. More charging infrastructure also translates to transparent pricing, which lets users prepare financially and align their travel plans.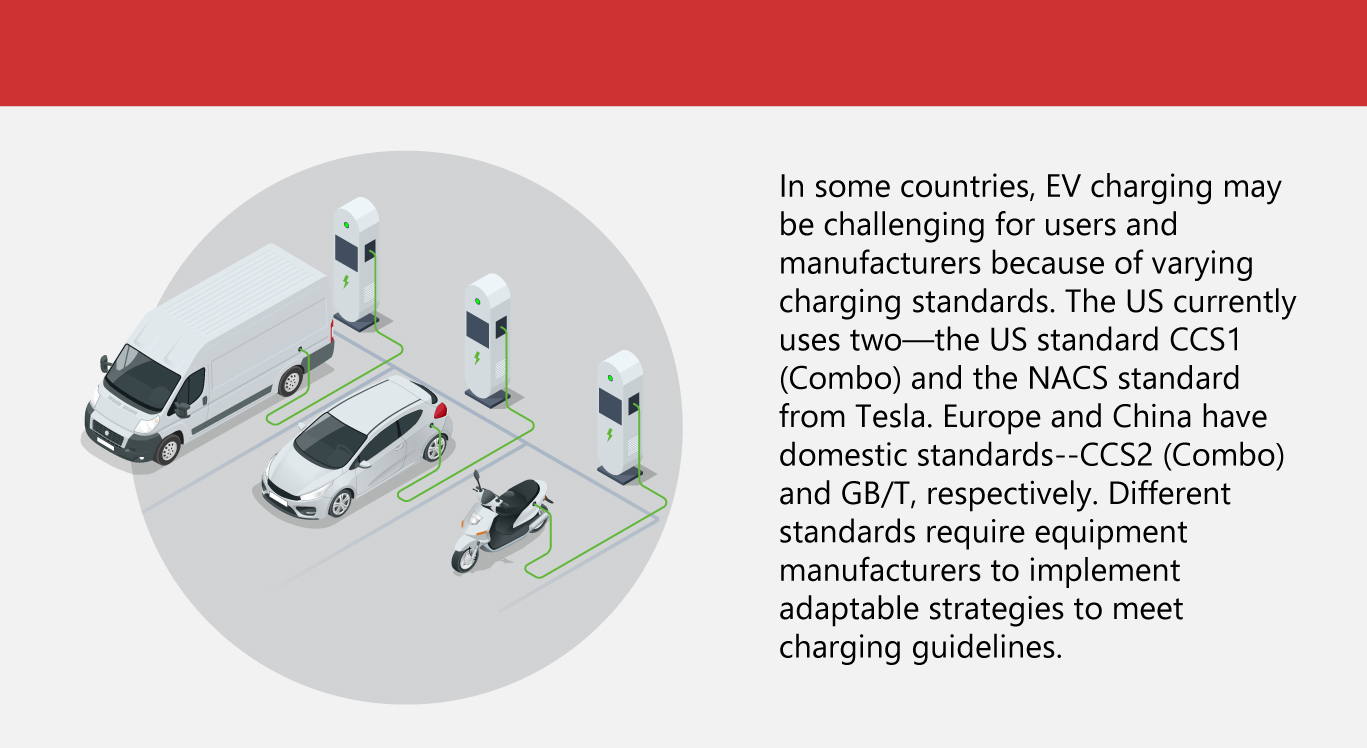
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog




