Top Trends That Shape Automated Testing
Global spending on testing solutions is projected to rise sharply, reaching $52.7 billion by 2027 from $24.7 billion in 2022, growing at an annual rate of 16.4%.
Crucial to this development are test automation frameworks, which provide the structure and standards for building, running, and managing automated tests. By reducing redundancy and boosting maintainability, they streamline product testing across environments and technologies, enabling teams to scale efficiently while adapting to diverse project needs.
Why automated testing frameworks matter: 5 benefits
Test automation frameworks bring order and consistency, enabling manufacturing solutions to reduce effort and build more sustainable, long-term testing practices.
- Streamlined & manageable tests
Without a framework, validation processes can become fragmented and difficult to manage. A structured system centralizes data and methods, ensuring consistency and oversight. For quality teams, this strengthens reliability testing by unifying processes and supporting long-term sustainability.
- Precision & DevOps alignment
Manual processes invite errors, while automated frameworks ensure consistency and repeatability. Integrated into development and operational pipelines, they validate each update automatically, accelerating product development, improving quality, and detecting issues early across industries.
- Simplified upkeep
As global manufacturing advances with new features and improvements, manually adjusting validation processes can drain time and resources. A framework streamlines product validation by centralizing updates—so a single change, like modifying safety standards, applies across multiple tests with consistency and efficiency.
- Reusable tests
Reusable automated tests help design and engineering teams cut repetitive work by applying the same scripts across projects and updates. Studies show this can reduce testing cycles by up to 40%, improving operational efficiency and freeing teams to focus on innovation and higher-value engineering tasks.
- Scalability
Automated testing frameworks easily handle growing volumes of tests as products expand in complexity. They run large test suites simultaneously across varied environments and platforms, achieving broad coverage without multiplying resources or time. Whether managing extensive validation regimes or adjusting to evolving engineering workflows, these future-ready frameworks offer scalable efficiency that manual methods cannot match.
(Also read: 40% Output Boost: IMI Reinvents PCBA Testing)
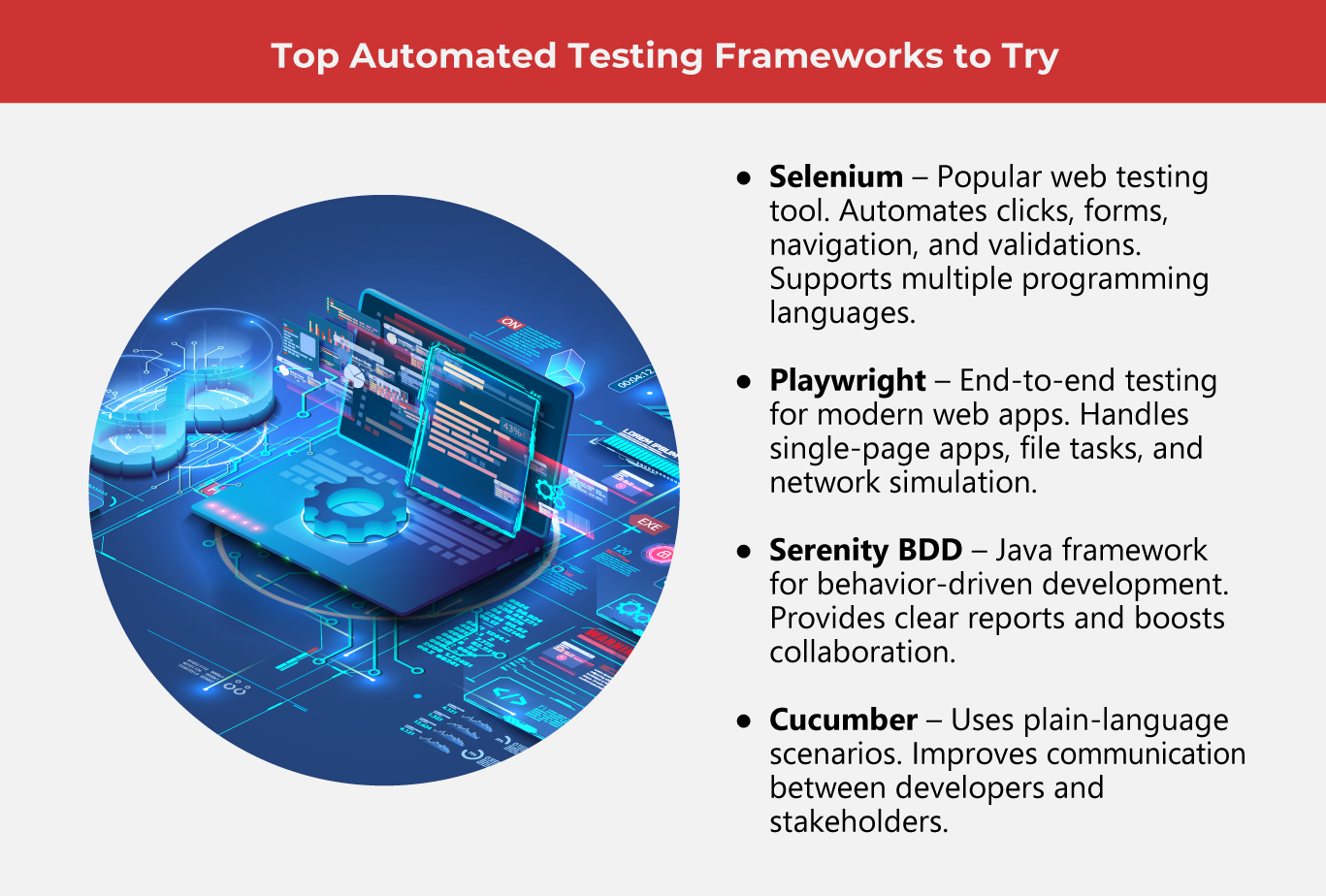
7 frameworks for automated testing
Automated testing frameworks vary in design and purpose. Some are simple, while others emphasize growth, flexibility, and efficiency to support more complex projects.
- Linear
Also called Record-and-Playback, this framework executes scripted tests step by step in the exact order they were captured—no code reuse, modularization, or parameterization is involved. Ideal for beginners or small-scale testing, it allows rapid script creation without programming expertise. However, because each test stands alone, user interface (UI) changes force updates across all scripts, making maintenance cumbersome as the test suite expands.
- Data-driven
This methodology isolates test operations from the data itself, using external sources such as databases or spreadsheet files to provide input values and expected results, streamlining maintenance and improving flexibility. This approach supports system development by enabling one script to execute multiple scenarios with varied data sets. It enhances coverage and eases maintenance since updates occur in the data source rather than the test script.
- Modular-based
Here, the application is divided into independent functional modules such as login, search, or checkout, each with its own script. These modules can be reused to build complete test cases, improving maintainability and scalability during product introduction and beyond. Updates are easier since only the affected module needs changes. While efficient for complex systems, it requires upfront planning and programming expertise.
- Behavior-oriented
By promoting collaboration among developers, testers, and business stakeholders, this framework supports the product life profile by aligning tests with actual user needs. It relies on plain language scenarios written in formats like "Given, When, Then," which turn requirements into executable documentation. This method reduces miscommunication, ensures shared understanding, and speeds up feedback throughout the development cycle.
- Keyword-focused
Login, Click, and VerifyElement are examples of keywords used in this framework to separate test steps from the underlying code. Testers design scenarios in tables or spreadsheets using these predefined action words, while a driver script executes them. This structure improves reuse, simplifies maintenance, and allows non-technical users to participate in test creation.
- Library architecture
Shared function libraries group common tasks such as login, data validation, or file handling into reusable modules. This framework improves test script scalability by centralizing frequently used functions. It also simplifies updates since changes in a library automatically apply to all dependent tests. Maximizing code reuse calls for thoughtful planning and skilled technical execution to implement and maintain the framework efficiently.
- Hybrid
Several testing automation frameworks integrate elements from both data-driven and keyword-driven approaches to create this framework. This combination allows for reusable functions and externalized test data, enhancing maintainability and scalability. By leveraging the strengths of multiple frameworks, it provides flexibility and adaptability in test case design and execution. This approach is particularly effective for complex applications requiring diverse testing strategies.
(Also read: Driving Precision Forward: IMI’s Award-Winning Stray Light Tester for Automotive Cameras )
Major trends influencing automated testing growth
Identifying the key trends behind this growth enables businesses to stay ahead and implement the most effective testing strategies.
- The rise of AI
Artificial intelligence helps speed up test development, broaden the scope of coverage, and simplify ongoing maintenance tasks. It enables self-healing tests that adapt to UI changes, automates repetitive tasks, and provides insights for better decision-making. Additionally, AI can predict potential failure points by analyzing historical data, leading to more reliable testing.
- Software robotics
Software robotics, or Robotic Process Automation (RPA), mimics tester actions to execute repetitive tasks. Configurable bots can learn processes quickly, cutting time and costs. RPA is forecast to grow from $3.17 billion in 2022 to $13.39 billion by 2030. AI advancements will enable smarter bots to tackle complex testing autonomously.
- Cloud-driven testing
With this, teams can execute tests across multiple platforms and devices without heavy on-premises infrastructure. It enables adaptable, cost-effective environments, accelerates test execution, enhances collaboration, and seamlessly integrates with continuous integration and delivery pipelines. Cloud testing simplifies complex workflows while supporting efficient, cross-platform quality assurance
- Blockchain testing
Blockchain testing ensures that distributed ledger applications function securely, reliably, and as intended. By automating validation of transactions, smart contracts, and network interactions, teams can detect vulnerabilities faster. This trend is gaining traction as organizations seek to reduce manual testing effort and streamline verification across decentralized platforms.
- Codeless approach
By doing away with writing code, users can design and run tests through intuitive visual interfaces. Drag-and-drop tools, recording, and playback features let business analysts and quality assurance professionals create automated tests quickly. This approach enables teams to focus on improving software quality without programming skills.
Automated testing continues to evolve, driven by innovations. These trends not only fast-track test execution but also improve accuracy, collaboration, and efficiency across development teams. By embracing these frameworks and technologies, businesses can reduce errors, enhance product quality, and stay competitive in a rapidly changing software landscape, ensuring their applications meet modern performance and reliability standards.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog




